可重入独占锁ReentrantLock
可重入独占锁ReentrantLock
# 前言
ReentrantLock是基于AQS框架的应用实现,具备AQS中的以下特性
阻塞等待队列 独占 公平/非公平 可重入 允许中断
ReentrantLock的核心实现
1.自旋 + CAS操作
2.CLH队列
双向队列AQS当中的同步等待队列也称CLH队列,CLH队列是Craig、Landin、Hagersten三人 发明的一种基于双向链表数据结构的队列,是FIFO先入先出线程等待队列,Java中的CLH队列是原CLH队列的一个变种,线程由原自旋机制改为阻塞机制。
3.LocksSuport
LockSupport.park(thread);LockSupport.unpark(thread);
# 1 加锁过程(非公平)
final void lock() {
//通过cas方式将state变量从0改为1,成功则将当前线程设置到exclusiveOwnerThread变量
if (compareAndSetState(0, 1))
setExclusiveOwnerThread(Thread.currentThread());
//否则请求加锁
else
acquire(1);
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
public final void acquire(int arg) {
//尝试加锁
if (!tryAcquire(arg) &&
//加锁失败则以当前线程构建节点入队列(addWaiter)
//更新前驱节点(上一节)点状态(可唤醒),并park住线程等待唤醒,唤醒后检查前驱节点是否头结点,是头节点则尝试加锁,加锁失败继续自循环park住线程
acquireQueued(addWaiter(Node.EXCLUSIVE), arg))
//前面中断唤醒过,则需要进行复位,恢复原先的中断状态
selfInterrupt();
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
protected final boolean tryAcquire(int acquires) {
//非公平锁实现
return nonfairTryAcquire(acquires);
}
final boolean nonfairTryAcquire(int acquires) {
final Thread current = Thread.currentThread();
int c = getState();
if (c == 0) {
//state为0时,尝试加锁(即设置state为1)
if (compareAndSetState(0, acquires)) {
//加锁成功则设置exclusiveOwnerThread变量为当前线程
setExclusiveOwnerThread(current);
//返回加锁成功
return true;
}
}
//state!=0且exclusiveOwnerThread变量等于当前线程
//则state累加(可重入锁的实现)
else if (current == getExclusiveOwnerThread()) {
int nextc = c + acquires;
if (nextc < 0) // overflow
throw new Error("Maximum lock count exceeded");
setState(nextc);
//返回加锁成功
return true;
}
//否则返回加锁失败
return false;
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
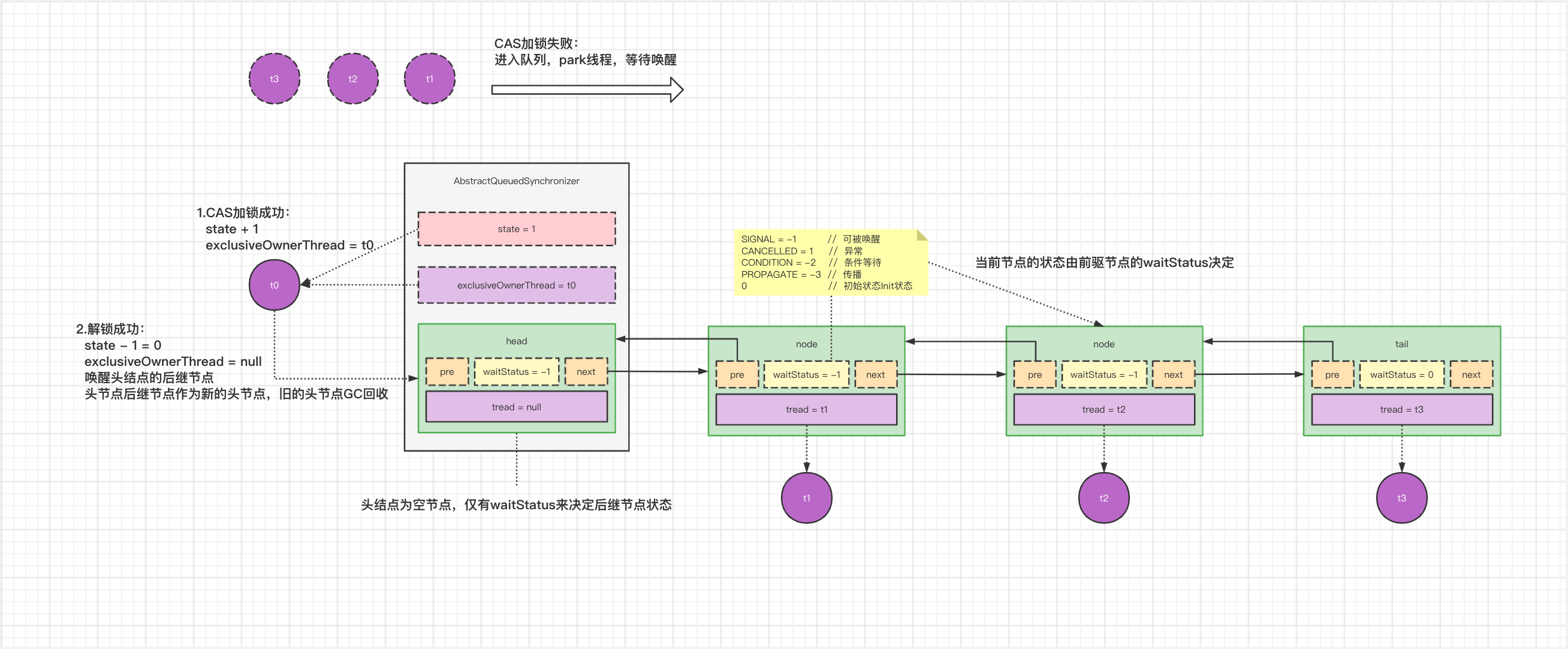
Node 重要属性
SHARED 共享属性 EXCLUSIVE 独占属性
static final Node SHARED = new Node();
static final Node EXCLUSIVE = null;
pre next thread
前驱节点, 下一节点, 当前线程
waitStatus 节点的生命状态
SIGNAL = -1 // 可被唤醒
CANCELLED = 1 // 代表出现异常,中断引起的,需要废弃结束
CONDITION = -2 // 条件等待
PROPAGATE = -3 // 传播
0 - 初始状态Init状态
private Node addWaiter(Node mode) {
//用当前线程为入参创建一个节点(独占属性)
Node node = new Node(Thread.currentThread(), mode);
Node pred = tail;
//如果尾节点不为空
if (pred != null) {
//则设置当前节点的前驱节点为尾节点
node.prev = pred;
//将当前节点更新为尾节点
if (compareAndSetTail(pred, node)) {
//更新成功则把前尾节点的下一个节点指向当前节点
pred.next = node;
//返回当前节点
return node;
}
}
//往队列添加当前节点
enq(node);
return node;
}
private Node enq(final Node node) {
for (;;) {
Node t = tail;
//如果尾节点为空(即队列为空)
if (t == null) {
//设置头结点
if (compareAndSetHead(new Node()))
//同时,头结点也是尾节点
tail = head;
//如果尾节点不为空
} else {
//则设置当前节点的前驱节点为尾节点
node.prev = t;
//将当前节点更新为尾节点
if (compareAndSetTail(t, node)) {
//更新成功则把前尾节点的下一个节点指向当前节点
t.next = node;
//返回当前节点
return t;
}
}
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
final boolean acquireQueued(final Node node, int arg) {
boolean failed = true;
try {
boolean interrupted = false;
for (;;) {
//p = 当前节点的上一个节点
final Node p = node.predecessor();
//如果当前节点的上一个节点是头结点,并且加锁成功
if (p == head && tryAcquire(arg)) {
//将当前节点设置为头结点
setHead(node);
//旧头结点让GC回收
p.next = null; // help GC
failed = false;
return interrupted;
}
//1.前驱节点状态为可唤醒,则当前节点所属线程可以park住
//2.park住线程;清除线程的中断标识,并返回清除之前的状态
if (shouldParkAfterFailedAcquire(p, node) &&
parkAndCheckInterrupt())
interrupted = true;
}
} finally {
if (failed)
//出现异常时才执行,几率非常低
//不过用lockInterruptibly()加锁时,如果用中断唤醒,会执行这个方法
cancelAcquire(node);
}
}
private void setHead(Node node) {
//头结点的属性基本都为空,只有一个waitStatus属性用来判断下一节点是否可被唤醒等
head = node;
node.thread = null;
node.prev = null;
}
private static boolean shouldParkAfterFailedAcquire(Node pred, Node node) {
int ws = pred.waitStatus;
//-1 前驱节点的状态为可唤醒,则返回true
if (ws == Node.SIGNAL)
return true;
//前驱节点的状态为异常,则依次往前找,直到非异常节点,将其下一节点指向当前节点。返回false
if (ws > 0) {
do {
node.prev = pred = pred.prev;
} while (pred.waitStatus > 0);
pred.next = node;
//否则,前驱节点状态设置为可唤醒。返回false
} else {
compareAndSetWaitStatus(pred, ws, Node.SIGNAL);
}
return false;
}
private final boolean parkAndCheckInterrupt() {
//重要!park住线程
LockSupport.park(this);
//清除线程的中断标识,并返回清除之前的状态
return Thread.interrupted();
}
private void cancelAcquire(Node node) {
if (node == null)
return;
//当前节点线程置为空
node.thread = null;
//当前节点前驱节点
Node pred = node.prev;
while (pred.waitStatus > 0)
//前驱节点状态为异常,则一直往前找,直到节点状态正常,将其置为当前节点的前驱节点
node.prev = pred = pred.prev;
//前驱节点的下一节点
Node predNext = pred.next;
//当前节点状态置为异常(取消)
node.waitStatus = Node.CANCELLED;
//如果当前节点为尾节点,则尝试把前驱节点设为尾节点
if (node == tail && compareAndSetTail(node, pred)) {
//设置成功则把前驱节点的下一节点也置为空
compareAndSetNext(pred, predNext, null);
} else {
//当前节点不是尾节点时:
int ws;
//如果 前驱节点不是头结点
//且 (前驱节点的状态是可唤醒 或者 前驱节点是非异常状态去尝试改成唤醒状态)
//且 (前驱节点的线程不为空)
if (pred != head &&
((ws = pred.waitStatus) == Node.SIGNAL ||
(ws <= 0 && compareAndSetWaitStatus(pred, ws, Node.SIGNAL))) &&
pred.thread != null) {
Node next = node.next;
//当前节点的下一节点不为空 且 状态不为异常
if (next != null && next.waitStatus <= 0)
//将前驱节点的下一节点指向 当前节点的下一节点
compareAndSetNext(pred, predNext, next);
} else {
//前驱节点是头结点时
//唤醒当前节点的下一节点
unparkSuccessor(node);
}
node.next = node; // help GC
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
# 2 解锁过程
public void unlock() {
sync.release(1);
}
public final boolean release(int arg) {
//更新state变量(state - 1),state为0时返回结果为true
if (tryRelease(arg)) {
Node h = head;
//
if (h != null && h.waitStatus != 0)
unparkSuccessor(h);
return true;
}
return false;
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
protected final boolean tryRelease(int releases) {
// state = state - 1
int c = getState() - releases;
//当前独占线程变量exclusiveOwnerThread不等于当前线程,则抛异常
if (Thread.currentThread() != getExclusiveOwnerThread())
throw new IllegalMonitorStateException();
boolean free = false;
if (c == 0) {
//如果state变为0,则返回标识置为true,当前独占线程变量exclusiveOwnerThread置为空
free = true;
setExclusiveOwnerThread(null);
}
//设置state
setState(c);
return free;
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
private void unparkSuccessor(Node node) {
int ws = node.waitStatus;
if (ws < 0)
//头节点状态为非异常时,更新为初始状态0
compareAndSetWaitStatus(node, ws, 0);
//头结点的后继节点
Node s = node.next;
//头结点的后继节点为空,或者状态为异常时:
if (s == null || s.waitStatus > 0) {
//将头结点的后继节点置为空
s = null;
//从尾节点开始向前找,找到最靠近头结点并且状态不为异常的节点。最终unpark该节点上的线程。
for (Node t = tail; t != null && t != node; t = t.prev)
if (t.waitStatus <= 0)
s = t;
}
if (s != null)
//unpark后继节点的线程
LockSupport.unpark(s.thread);
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
# 3 加锁过程(公平)
final void lock() {
acquire(1);
}
1
2
3
2
3
protected final boolean tryAcquire(int acquires) {
final Thread current = Thread.currentThread();
int c = getState();
if (c == 0) {
// state为0时(锁未被占用),队列为空或者队列中的第一个为自己线程时,去尝试加锁
if (!hasQueuedPredecessors() &&
compareAndSetState(0, acquires)) {
setExclusiveOwnerThread(current);
return true;
}
}
else if (current == getExclusiveOwnerThread()) {
int nextc = c + acquires;
if (nextc < 0)
throw new Error("Maximum lock count exceeded");
setState(nextc);
return true;
}
return false;
}
public final boolean hasQueuedPredecessors() {
Node t = tail;
Node h = head;
Node s;
//头结点不等于尾节点(即队列不为空) 且 (头结点的后继节点为空 或者 头结点的后继节点线程不是当前线程)
return h != t &&
((s = h.next) == null || s.thread != Thread.currentThread());
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
公平锁与非公平锁的实现区别主要在上面两段代码:
- 非公平锁加锁开始时会直接通过cas的方式先去尝试加锁。公平锁没这个操作。
if (compareAndSetState(0, 1))
setExclusiveOwnerThread(Thread.currentThread());
2.公平锁方式在cas加锁前会先去判断队列是否已经有节点,有其他节点时去排队。